I first heard about micro cellular rubber from my brother-in-law, Dave, who runs a mid-size construction crew in western Pennsylvania. He slipped it into conversation the way contractors do with materials they quietly swear by — almost reluctantly, like he was giving away a trade secret. “We’ve been sealing window frames with it for three years,” he said. “Callbacks dropped almost overnight.”
That one conversation sent me down a rabbit hole I haven’t fully climbed out of. And honestly? I’m glad.
So What Exactly Is Micro Cellular Rubber?
Micro cellular rubber is a type of expanded rubber material characterized by a closed or open cell structure with extremely fine, uniform cells — typically ranging between 0.1mm and 0.5mm in diameter. Unlike standard foam rubber, which can be coarse and compressible to the point of collapse, micro cellular rubber maintains structural memory. It compresses under load and returns to its original shape — repeatedly, without significant degradation.
It’s manufactured from materials like EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer), neoprene, silicone, and natural rubber. Each base material brings a different performance profile, which matters enormously depending on where and how it’s used.
Where It Shows Up in Home Construction
Window and Door Sealing This is where most American homeowners unknowingly benefit from micro cellular rubber already. The compression seals around double-pane windows and exterior doors in modern builds are frequently made from EPDM-based micro cellular rubber. It handles temperature swings from -40°F to over 250°F without cracking or hardening — critical in climates like Minnesota winters or Arizona summers.
Flooring Underlayment Micro cellular rubber underlayment beneath hardwood or laminate flooring reduces impact noise transmission by up to 20 decibels in some product tests. If you’ve walked into a room and noticed how “solid” the floor felt underfoot, there’s a reasonable chance micro cellular rubber had something to do with it.
HVAC Pipe and Duct Insulation Closed-cell micro cellular rubber wraps around refrigerant lines and ductwork to prevent condensation and heat loss. It outperforms fiberglass wrap in humid climates because it doesn’t absorb moisture, which means no mold risk hiding inside your walls.
Garage Door Bottom Seals The flat rubber strip at the base of your garage door? Often micro cellular rubber. It conforms to uneven concrete, blocking drafts, water intrusion, and pests — three of the most common garage complaints in American homes.
Vibration Dampening Under Appliances Washing machines, HVAC compressors, and refrigerators generate low-frequency vibration that transfers through floors and walls. Micro cellular rubber anti-vibration pads placed under these units measurably reduce noise transmission — a detail that matters more in townhomes and multi-story houses.
A Real-World Testimonial
Sandra K., a homeowner in Austin, Texas, had her home retrofitted with micro cellular rubber door seals after noticing a persistent draft and a 12% spike in her winter heating bills. “After the installer swapped out the old foam strips, I ran my hand along the door frame on a cold night and just… felt nothing. No draft. It was the most satisfying $180 I’ve ever spent on this house.”
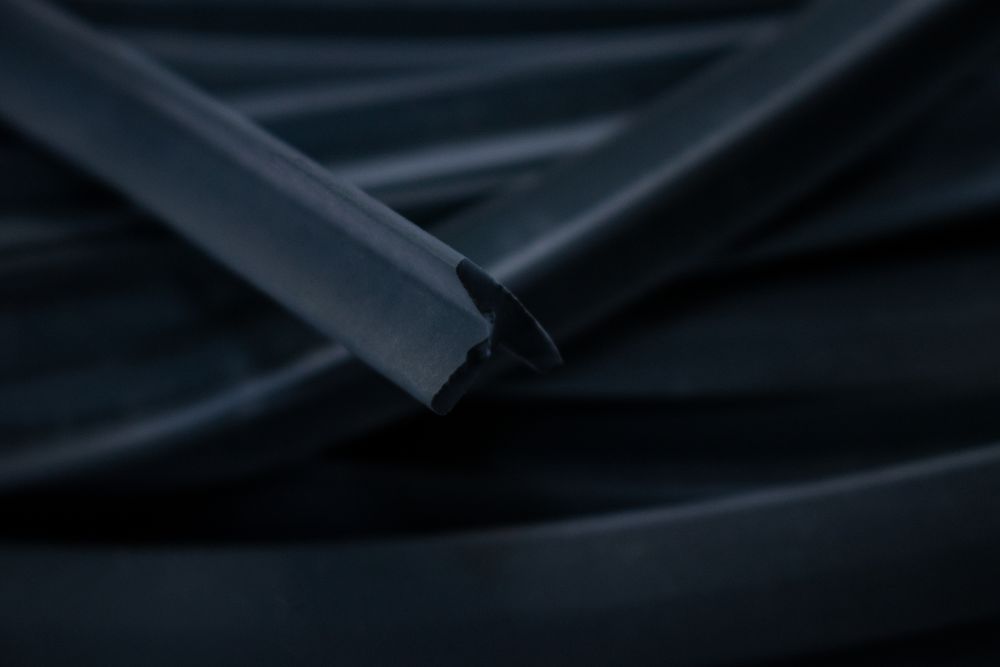

FAQs About Micro Cellular Rubber
Q: Is micro cellular rubber the same as regular foam weather stripping? No. Standard foam weather stripping uses an open-cell structure that degrades quickly and loses compression memory within one to two heating seasons. Micro cellular rubber retains its shape under repeated compression cycles, often lasting 10 to 20 years depending on UV and chemical exposure.
Q: Can I install micro cellular rubber products myself? Many applications — door seals, appliance pads, underlayment strips — are DIY-friendly. Products come with adhesive backing and can be cut with scissors or a utility knife. HVAC pipe insulation is slightly more involved but manageable for a confident DIYer.
Q: Is micro cellular rubber safe for indoor use? EPDM and silicone-based micro cellular rubber products are generally non-toxic and low-VOC. Look for products that comply with ASTM standards and carry UL certifications if you’re installing in enclosed spaces.
Q: How does micro cellular rubber perform in extreme climates? Extremely well. EPDM micro cellular rubber is specifically rated for UV resistance and temperature extremes, making it a preferred choice in states with significant seasonal temperature variance like Colorado, Michigan, and Texas.
Q: Where can I buy micro cellular rubber for home use? Specialty weatherization suppliers, industrial rubber distributors, and large-format home improvement stores carry it in sheet, strip, and roll forms. Always confirm the cell structure (open vs. closed) and durometer rating before purchasing — these specs determine how the material will perform in your specific application.
There’s something satisfying about materials that do exactly what they’re supposed to do, year after year, without demanding any attention. Micro cellular rubber is that kind of material — understated, reliable, and genuinely useful in ways most homeowners never think about until something goes wrong.
Dave put it well during that Pennsylvania conversation: “The best installation is the one nobody ever calls you about.” By that measure, micro cellular rubber might be one of the best materials in the business.